A tier 4 diesel generator gives strong power and follows strict rules for pollution. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) makes these rules to stop bad chemicals from getting out. Tier 4 generators are different from regular industrial diesel generators. They help lower air pollution. Using them helps keep the air clean and makes the environment healthier.
Tier 4 Generators Overview

Definition and EPA Tier Ratings
Tier 4 generators are the newest type in the EPA tier ratings for diesel engines. These generators follow the strictest rules from the Environmental Protection Agency. The EPA made these ratings to help cut down on bad pollution from industrial diesel generators. Tier 4 rules started in 2004 and were put in place between 2008 and 2015. These rules make sure there is a big drop in particulate matter and nitrogen oxides.
Note: Emergency generators do not have to follow Tier 4 rules. They only need to meet Tiers 2 and 3.
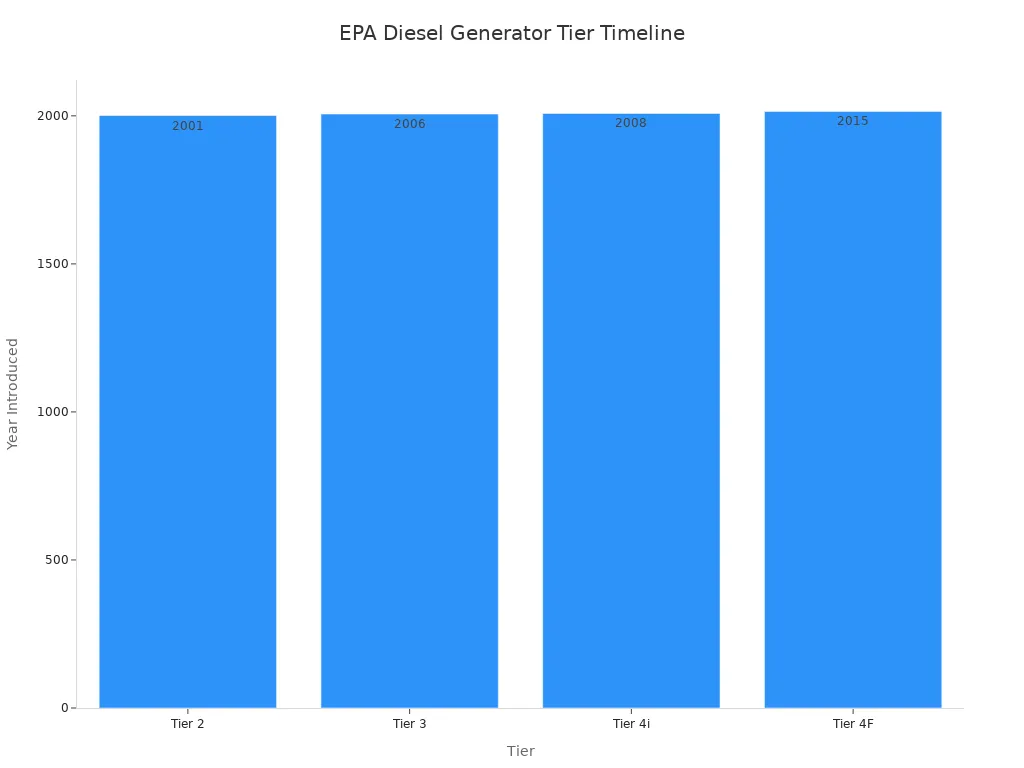
Here is a table that shows the EPA tier ratings for diesel generators:
| Tier | Year Introduced | Emission Reductions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 2 | 2001 | Stricter rules for NOx, HC, DPM | Phased in over five years |
| Tier 3 | 2006-2008 | Another step closer to Tier 4 | Needed starting in 2007 |
| Tier 4i | 2008 | 95% less PM, 90% less NOx | Transitional phase |
| Tier 4F | 2008-2015 | 95% less PM, 90% less NOx | All classes by 2015 |
Tier 4 generators are special because they use ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel and smart engine technology. When you use these generators, you get cleaner air and a better environment.
How Tier 4 Generators Work
Tier 4 generators use new engineering to meet tough emission rules. These generators have more advanced engine designs than older ones. They use electronic controls to make fuel injection and burning better. This means they use fuel more efficiently and make less pollution.
Here is a table that compares Tier 4 generators with older tiers:
| Feature | Tier 4 Generators | Earlier Tiers |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Reduction Technologies | Advanced (EGR, SCR, DPF) | Limited or none |
| Engine Design | Bigger, more complex, electronic controls | Simpler mechanical |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better atomization and burning | Not as good |
| Maintenance | More advanced technology | Easier requirements |
More people are using Tier 4 generators now. Companies keep making new models to meet stricter rules and the need for reliable power.
Emission Control Technologies
Tier 4 generators use different emission control technologies to keep pollution low. The most common systems are:
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): This system uses diesel exhaust fluid, which is a safe mix of urea and water. When added to the exhaust, it reacts with NOx gases and turns them into nitrogen and water vapor. SCR can lower NOx emissions by over 95%.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): EGR cools the engine by sending some exhaust back inside. This helps stop NOx from forming. EGR systems can also lower NOx by over 95%.
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) and Wall Flow Filtration: These filters catch tiny particles before they leave the exhaust. The trapped stuff is then burned up and released as nitrogen gas and carbon dioxide.
Here is a table that explains these technologies:
| Technology | Description | Emission Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| SCR | Uses DEF to change NOx into nitrogen and water | Over 95% NOx |
| EGR | Sends exhaust back to cool the engine and lower NOx | Over 95% NOx |
| DPF/Wall Flow Filtration | Catches and burns particles for cleaner exhaust | Up to 95% PM |
Tip: DEF is safe to use and easy to store. You just need to refill it sometimes to keep your generator working well.
With these systems, Tier 4 generators cut particulate matter by 95% and nitrogen oxides by 90% compared to older standards. You will also see less sulfur and better air quality near your generator.
Tier 4 vs. Industrial Diesel Generator Standards
Key Differences from Tier 3
There are big changes between Tier 4 and Tier 3 generators. The EPA made Tier 3 rules from 2006 to 2008. Tier 4 rules came later and are much stricter. Tier 4 generators use advanced after-treatment systems. Tier 3 models use in-cylinder controls instead. This means Tier 4 generators make much less pollution.
| Feature | Tier 3 | Tier 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction Period | 2006-2008 | 2008-2012 |
| Emission Reduction | Reduced NOx and PM | Up to 90% reduction in NOx, PM |
| Technology | In-cylinder combustion controls | Advanced after-treatment systems |
| Particulate Matter Emission | Higher than Tier 4 | 90% less than Tier 3 |
| Hydrocarbons and Sulfur | Higher than Tier 4 | Significantly reduced |
| Carbon Monoxide Levels | Similar to Tier 4 | Similar to Tier 3 |
EPA and other experts say Tier 4 generators are the cleanest. They are better than all other industrial diesel generator types.
Regulatory Requirements and EPA Tier Ratings
If you use an industrial diesel generator, you must follow EPA rules. These rules are strict for most businesses and construction sites. EPA Tier 4 rules are for non-road diesel engines. They focus on engines with 56 kW or more. The rules help lower particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and air toxins. The New Source Performance Standards set limits for big stationary generators. These standards help keep the air clean. They also try not to hurt businesses.
- Tier 4 rules are for most new non-road industrial diesel generator models.
- Emergency generators have different rules. They may only need to meet Tier 2 or Tier 3 standards.
- The EPA changes these rules as technology gets better. This helps protect people’s health.
Performance, Efficiency, and Maintenance
Tier 4 generators use fuel better and make less noise. They also help keep the air cleaner than older models. You see the most benefits when the generator works hard. But Tier 4 generators need more care and maintenance.
| Feature | Tier 3 Generators | Tier 4 Generators |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate improvements | Superior, especially at high loads |
| Operational Costs | Lower, simpler maintenance | Higher, due to advanced systems |
| Emissions Control | Moderate reductions | Superior emissions control |
| Maintenance Complexity | Simpler, less frequent | More complex, needs specialized care |
You need to clean or change diesel particulate filters for Tier 4 models. You also have to refill diesel exhaust fluid. These jobs make your maintenance list longer. But you get cleaner air and save money on fuel over time. EPA and experts say you should check your generator often. This keeps it working well.
Tip: Always follow the manufacturer’s maintenance plan for your industrial diesel generator. This helps you follow the rules and avoid expensive repairs.
Benefits of Tier 4 Generators

Environmental Impact
When you pick tier 4 generators, you help the planet. These generators use new technology to lower bad gases and particles.
- Tier 4 generators cut nitrogen oxides (NOx) by about 93% from old models.
- They also drop particulate matter (PM) by around 94%.
- Cleaner air helps your town and makes the air better for everyone.
When generators make less pollution, everyone breathes healthier air.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Tier 4 generators use fuel better than old ones. They have improved cooling, oil, and fuel systems. These parts help you use less fuel and save money. The EPA rules make companies build engines that waste less energy. You spend less on fuel because these generators work more efficiently.
| Evidence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved efficiency | EPA-approved generators use about 5% less fuel. |
| Lower operational costs | Better performance means you pay less for fuel and repairs. |
| Reliable maintenance | Regular care keeps your generator working and saves money. |
Reliability and Compliance
Tier 4 generators give steady power you can trust. They last a long time before breaking down, often over 50,000 hours. This means you have fewer power problems. Smart maintenance helps keep the generator running more than 99.6% of the time. Fast checks with smart tools also fix problems quicker.
| Metric | Description | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| MTBF | Time between big breakdowns | Over 50,000 hours, fewer problems |
| System Availability | Uptime with smart maintenance | Over 99.6% uptime |
| Failure Rate Analysis | AI tools find problems fast | 68% quicker problem finding |
Tier 4 generators also meet emissions rules. Special parts like diesel particulate filters, selective catalytic reduction, and exhaust gas recirculation help you follow EPA and state laws. Using ultra-low sulfur diesel keeps your generator and the environment safe.
You get lots of good things with tier 4 generators.
- These machines use smart systems like SCR and DPF to cut pollution.
- They follow EPA tier 4 final rules, so you meet tough laws.
- You get less noise and save fuel.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Emissions Control | Cleaner air and following the rules |
| Fuel Efficiency | Cheaper costs and better for the planet |
Experts and the EPA say tier 4 generators give strong, clean power you can trust.
FAQ
What fuel do Tier 4 diesel generators use?
Tier 4 generators need ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel. This kind of fuel helps make less pollution. It also helps the generator meet EPA rules.
Do you need special maintenance for Tier 4 generators?
Yes, you do. You have to check the emission systems often. You also need to refill diesel exhaust fluid and clean the filters. Always use your manufacturer’s guide for the best care.
Where can you find official Tier 4 emission standards?
You can find the Tier 4 emission standards on the EPA website.
For more information, go to EPA.gov.
